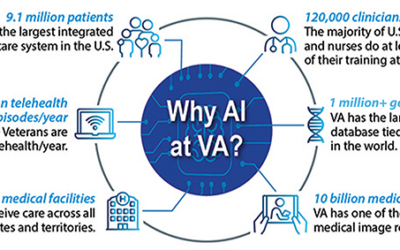
The speed at which artificial intelligence (AI) is being embraced at the VA has legislators both hopeful and concerned, optimistic that it can improve veterans’ health but worried about data privacy and the possibility of software superseding human decision-making in clinical settings.
VA Study: Microbial Contamination Continues in Hospitals, Even When Recommended Cleaning Protocols Are Followed
Microbial contamination—including pathogenic and potentially pathogenic bacteria—persisted on high-touch hospital surfaces despite compliance with recommended disinfection protocols, according to a study performed at the Central Texas Veterans Healthcare System.
How Veterans With TBI, GWI Present With Frontotemporal Disorders
Frontotemporal lobe disorders (FTD), which affect personality, behavior and language, are among the most common brain neurodegenerative disorders.
Even Mild COVID-19 Infections Caused Impaired Fitness in Military Personnel
Healthy, young members of the military who have had COVID-19 may experience impairments in fitness up to a year after their acute illness has resolved
Very Elderly Patients Fare Much Worse When Treated for DLBCL
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) becomes much more difficult to treat in older patients, according to a new study suggesting that more adults of advanced age be included in clinical trials for new agents.
Despite Disparities, Making a Difference for Veterans With Relapsed DLBCL
DURHAM, NC—Recent Food and Drug Administration approvals of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapies and novel immunotherapies have helped to significantly improve outcomes for patients with relapsed and refractory diffuse large B cell lymphoma (R/R DLBCL)....
More Diverse Dataset Raises Questions about MGUS Risk Models
Patients with monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) have been thought to have a less than 1% chance of progressing to multiple myeloma as long as their M-protein levels are below 1.5 g/dL.
For CLL, BTK Inhibitors Appear to Extend Time to Next Line Most
JACKSONVILLE, FL—As treatment options for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) multiply, physicians face an increasing array of sequencing options but have little guidance from clinical trials of the most effective order given each patient’s specific disease...
New Factbook Reveals Veteran Trends, Including Mental Health, Labor Market
U.S. military veterans are declining as a percentage of the population and are, on average, older, more likely to be male and less racially or ethnically diverse than the overall nonveteran population, reports a new factbook that sheds light on demographics, mental health and labor market outcomes.
Surgery Is Better Treatment for Primary Aldosteronism
Even though primary aldosteronism (PA) is one of the most common causes of secondary hypertension, the comparative outcomes of targeted treatment often are unclear.
Consensus Documents Answers Some Questions on Carotid Stenosis
Many national/international guidelines provide recommendations on management of patients with asymptomatic (AsxCS) and symptomatic (SxCS) carotid stenosis. Several questions remain unanswered, however, according to a new report.
SMART2 CABG Risk Score Performs Well in Racially Diverse VA Cohort
A new study tested the potential of the Secondary Manifestations of Arterial Disease (SMART2) risk score for use in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG).
VA’s Research Portfolio Suffers From Lack of Focus, Critics Maintain
VA’s research portfolio has slowly but steadily grown larger year after year. Nearly every major piece of legislation impacting VA includes provisions requiring the department to conduct research, whether it be on toxic exposure, mental health, suicide or other high-profile issues affecting veterans’ health.
Thyroid Cancer More Common Among Transgender Female Veterans
Transgender female veterans appear to have a high prevalence of thyroid cancer, according to a recent study that might be the first to demonstrate such a disparity in that cohort.
MHS Patients Receive Earlier Cancer Diagnoses Than General U.S. Population
Cancer patients treated within the MHS generally receive their diagnoses earlier than members of the general U.S. population covered by employee-provided insurance, Medicaid or without insurance.
Apixaban Suggested as Better OAC for Frail Older Adults With AF
Past research has suggested that elderly veterans who are frail are less likely to be prescribed oral anticoagulants for atrial fibrillation (AF). A recent study suggested a possible way to mitigate some of those challenges.
MGUS Higher in Servicemembers, No Association Seen With Burn Pit Exposure
Individuals who have served in the U.S. military have about three times the risk of monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) as a similarly aged cohort in the Icelandic iStopMM study.
Mental Health Issues Increase Mortality in Some Veterans With AML
Venetoclax combinations are common treatments for individuals with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who are unable to withstand the rigors of intensive induction chemotherapy.
BTK Inhibitors Provide Option for CLL Patients With Severe Renal Dysfunction
BTK inhibitors have proven to be a powerful tool in CLL treatment and have replaced chemoimmunotherapy as the preferred first-line treatment.
Evaluate Veterans With MGUS for Cardiovascular Disease
Monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS) is not considered a hematological condition of concern, yet it is associated with lower overall survival. VA researchers led by Lawrence Liu, MD, of the St. Louis VAMC, explored whether the reduced life expectancy arose from an increased risk of cardiovascular events.
Deployment Linked to Longer Survival in Servicemembers, Veterans With NHL
A study presented at the 2023 ASH Conference, provided additional evidence for the healthy deployer effect, this time in individuals with non-Hodkin lymphoma.
Which Veterans Should Undergo SPEP Testing for Plasma Cell Dyscrasia?
Plasma cell dyscrasia affects up to 5% of adults. While often asymptomatic, its characteristic clonal expansion of bone marrow plasma cells can also indicate the presence of several hematological malignancies including multiple myeloma.
GLP-1 Use Reduces Risk of MGUS Progression in Some Veterans
Glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists have gained huge popularity as they have demonstrated the ability to substantially reduce both blood-glucose levels and weight. In addition, recent research suggests cardiovascular and renal benefits to their use in certain populations.
Agent Orange Increases CVD Risk in Veterans With Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
As Vietnam-era veterans move into the age range in which most myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) develop, the VA has a keen interest in fully understanding the full impact of exposure to Agent Orange in veterans with these malignancies.
Million Veteran Program Study Pinpoints Concerns About Cannabis-Use Disorder
A study using data from the VA’s Million Veteran Program raised serious concerns about risks associated with cannabis use.
New Strategic Lab Director Fosters Disruptive Technologies, Seeks Growth
As the executive director of VA’s brand-new Strategic Initiatives Lab (Strat Lab), it is the mission of Anne Lord Bailey, PharmD, BCPS, to encourage VA to play the long shots.
Not Just a Bulging Belly: DRA Causes Problems for Military Women
Diastasis recti abdominis (DRA) is a common condition in pregnant and postpartum women, occurring when the rectus abdominis muscles, commonly called the six-pack ab muscles, separate from being stretched.
Uterine Cancer Mortality Increased Sharply in Some Groups
Since the beginning of the 21st century, uterine cancer mortality has increased, especially among Black and Hispanic women, according to a new study.
Daily Naltrexone Use Doesn’t Negatively Affect Performance in Soldiers
Daily use of naltrexone, a medication that blocks the effects of opioids with minimal side effects, doesn’t adversely affect the physical, cognitive or marksmanship performance of U.S. Army soldiers, according to a recent study.
Liver Cancer Risk Low for Veterans Who Clear HCV Without Treatment
The risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma, the most common type of liver cancer, is low for veterans who spontaneously clear hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection.